Pipeline
Satya’s Pipeline comprises First-In-Class and Best-In-Class
Targets focused on DDR pathway and Oncogenes.
Targets focused on DDR pathway and Oncogenes.
TARGET
MOA / INDICATION
BIO MARKER
RIGHTS
EARLY DISCOVERY
LEAD OPTIMIZATION
PRE - CLINICAL
IND
RAD51
DDR; Pan-cancer across solid tumors
Replication Stress, Oncogene mutations
Global
87%
SOS1
Oncogene; NSCLC, CRC
EGFR mutation & Pan RAS mutation
Global
76%
Undisclosed
DDR/ Cell cycle
Undisclosed
Partnered
Undisclosed
KIF18A
DDR
CIN+ve cells
Global
49%
PARG
DDR
HRD
Global
35%
USP1
DDR
HRD
Global
9%
Pipeline
Satya’s Pipeline comprises First-In-Class and Best-In-Class
Targets focused on DDR pathway and Oncogenes.
Targets focused on DDR pathway and Oncogenes.
TARGET
MOA / INDICATION
BIO MARKER
RIGHTS
EARLY DISCOVERY
LEAD OPTIMIZATION
PRE - CLINICAL
IND
RAD51
DDR; Pan-cancer across solid tumors
Replication Stress, Oncogene mutations
Global
91%
SOS1
Oncogene; NSCLC, CRC
EGFR mutation & Pan RAS mutation
Global
77%
Undisclosed
DDR/ Cell cycle
Undisclosed
Partnered
Undisclosed
KIF18A
DDR
CIN+ve cells
Global
49%
PARG
DDR
HRD
Global
35%
USP1
DDR
HRD
Global
11%
RAD51
- The centrality and functionality of RAD51 in the DDR pathway confers upon it a broad role in various replication stress-induced cancers. Thus, there is a potentially wide patient base that can be treated with this class of drugs.
- Our candidate compound, by specifically targeting RAD51:BRCA2 inhibition: a) transiently prevents nuclear RAD51 foci formation; b) has no effect on RAD51 expression; c) does not affect any of the other functionalities of RAD51 (ATP hydrolysis, multimerization or DNA binding); and d) is unlikely to lead to overt toxicities
- The candidate compound is potent across tumors with high Replication Stress (GOF in RAS, EGFR, PI3K and other genes)
- SAT-122 can therefore be a Broad Spectrum oncology agent and used: a) in High Replication stress tumors; b) in combination with replication stress inducers such as Olaparib; and c) in combination with Chemotherapy and SOC drugs for RAS/ EGFR/ PI3K mediated tumors
Ref: Annals of Oncology 29: 1203–1210, 2018; Clinical Breast Cancer Volume 18, Issue 2, April 2018, Pages 184-188; Clin Cancer Res. 2017 November 01; 23(21):6708–6720 Cancer Cell International (2023) 23:231 BMB Rep. 2019; 52(2): 151-156] Plos one 17.8 (2022): e0266645. Cancers 13.12 (2021): 2930. Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 7003.
SAT-122, the IND-candidate, has demonstrated excellent efficacy in multiple solid tumor cell lines and xenograft models, as a single angle and in combinations
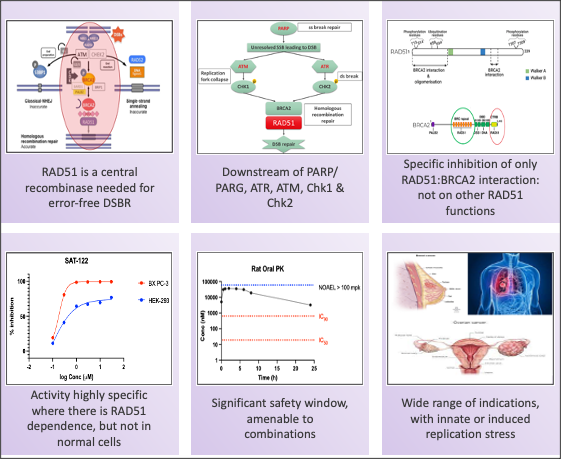
Drugging RAD51 via RAD51:BRCA2 disruption
SOS1
-
- SOS1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for RAS proteins involved in activating Ras. Inhibition of SOS1 results in lowering the Ras-GTP activated state, inhibiting the RAS-MEK-ERK pathway and lowering proliferation, in both WT and the various mutant Ras isoforms
- SOS1 inhibition is synthetic lethal with activating SHP2 mutations (10-20% of many of solid tumors).
- SOS1 acts as a potential driver in late stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) & Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) resistant mutant EGFR bearing cancers
Satya’s SOS1 inhibitors demonstrate complete pERK and pAKT inhibition across various cell lines and best-in-class efficacy in a KRAS driven cancer xenograft model.
Ref: Adapted from Cancers 15.20 (2023): 5015
Parg
- Despite the success of PARP inhibitors, drug resistance is a clinical hurdle. Loss of PAR glycohydrolase (PARG) is identified as a major resistance mechanism. PARG depletion restores PAR formation and partially rescues PARP1 signaling. Thus, PARG ihhibition provides an therapeutic opportunity to sensitize PARP inhibitors further.
- Additionally, PARG inhibition disrupts DNA damage repair cycle and leads to cell death. PARG depleted/ inhibited cells show increased sensitivity to DNA damage agents.
We anticipate identification of a differentiated candidate compound by end-2024
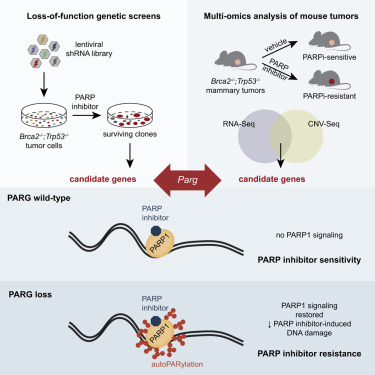
Eva Gogola et al, Cancer Cell June 2019
KIF18A
- Chromosomal instability (CIN), characterized by frequent mis-segregation of chromosomes during mitosis, is a hallmark of tumor cells caused by changes in the dynamics and control of microtubules that comprise the mitotic spindle. Thus, CIN +ve tumor cells may respond differently than normal diploid cells to treatments that target mitotic spindle regulation. KIF18A is required for proliferation of CIN +ve cells derived from triple negative breast cancer or colorectal cancer tumors but not in near-diploid cells. CIN +ve tumor cells exhibit mitotic delays, and increased cell death following inhibition of KIF18A. Sensitivity to KIF18A knockdown is strongly correlated with centrosome fragmentation. (Carolyn Marquis et al., Nature Communications, 2021).
Satya's KIF18A inhibitor is a highly differentiated best-in-class compound characterized by superior pharmacokinetic properties (clearance in 12 hrs compared to 48 hrs in competitor compounds) potentially leading to superior safety and druggability
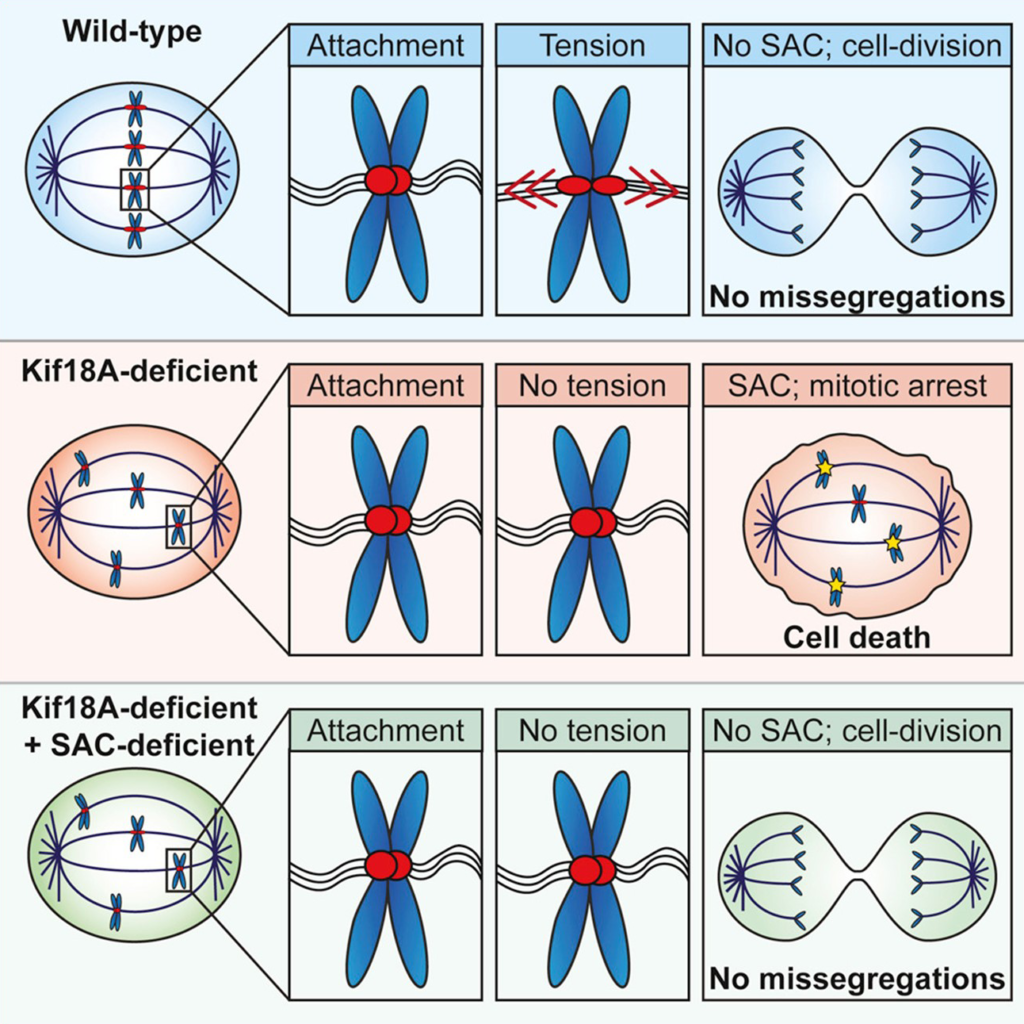
Louise Jannsen et al., Current Biology September 2018
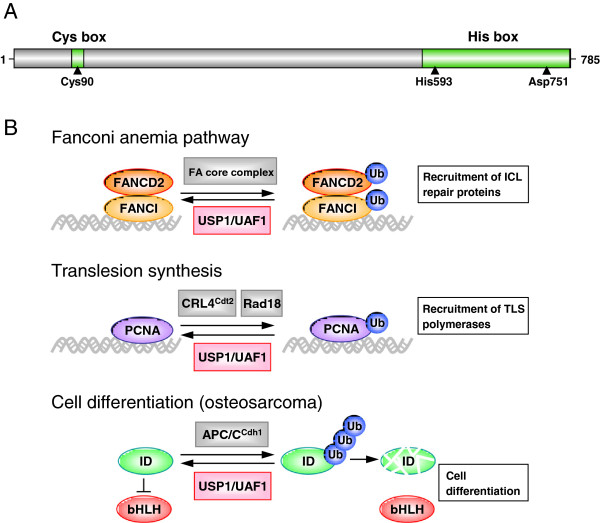
USP1
- USP1 represents a promising target for drug intervention because of its involvement in Translesion synthesis (TLS) and intra-strand crosslink repair important for normal DNA damage response
- The FA(Fanconi anemia) pathway regulates the repair of DNA crosslinks, a critical step in this pathway is the monoubiquitination and deubiquitination of FANCD2
- PCNA ubiquitination is central to the normal DNA damage response process in eukaryotes. Its deubiquitimation is important for translesion DNA synthesis.
- USP1 has been shown to deubiquitinate PCNA and FANCD2 in cells. Inhibition of USP1 causes ubiquitination of PCNA & FANCD2 leading to accummulation of damaged DNA leading to cell death